Ever wondered why some air conditioners cost more? Features matter, but a big part of the price difference is due to the SEER rating. This rating affects your energy bills all year. Understanding SEER ratings can improve your home comfort and save you money. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about SEER ratings. This will make buying an air conditioner easier.
Outline
ToggleWhat Is SEER Rating?
SEER rating stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Rating. It’s a metric used to gauge the efficiency of air conditioning units and heat pumps. The SEER rating of an AC unit tells you how much cooling it provides per unit of energy consumed. Essentially, it measures the ratio of cooling output over a typical cooling season divided by the electric energy input during the same period.
Understanding SEER ratings is crucial when selecting a new air conditioner. Systems with higher SEER ratings are more energy-efficient, which can significantly reduce electricity bills. In the US, the minimum SEER rating for air conditioners is 14 in the Southern States and 13 in the Northern States, but you can find units with SEER ratings as high as 25 or more. These high-efficiency models may cost more upfront but can offer substantial savings in the long run.
The concept of SEER is similar to miles per gallon in cars; just as a car with more miles per gallon is more fuel-efficient, an AC unit with a higher SEER is more energy-efficient. This efficiency can vary depending on several factors, including the type of air conditioner and the environment in which it’s used.
How Is SEER Rating Calculated?
Calculating the SEER rating of an air conditioner involves measuring the cooling output during a typical cooling season and dividing it by the total electric energy input during the same period. This process is done under standardized conditions to ensure consistency and fairness in ratings.
The formula for SEER is:
![]()
For example, if an air conditioner delivers 120,000 BTU of cooling and consumes 1,000 kWh of electricity throughout a cooling season, its SEER rating would be:
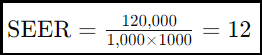
This means the unit provides 12 BTUs of cooling per watt-hour of electricity used. While this calculation might seem straightforward, it’s usually performed under controlled conditions by manufacturers and certified labs to ensure the unit’s efficiency rating is accurate and reliable.
Higher SEER ratings indicate greater efficiency and less energy consumption, which is crucial in regions with long, hot summers. However, it’s important to balance the SEER rating with other considerations like unit cost, the climate you live in, and the size of your home.
Benefits Of High SEER Ratings
Investing in an air conditioner with a high SEER rating can offer several benefits, making it a worthwhile consideration for homeowners:
- Reduced Energy Bills: The most immediate benefit of a high SEER rating is the potential for lower energy bills. Since these units are more efficient at converting electricity into cooling power, they require less energy to maintain a comfortable temperature in your home.
- Environmental Impact: High SEER ratings contribute to reduced energy consumption, which in turn decreases carbon emissions. This is crucial for reducing your household’s carbon footprint and combating climate change.
- Improved Comfort: Air conditioners with higher SEER ratings often include advanced features like variable-speed compressors and fans. These features allow for finer adjustments of cooling output, maintaining more consistent indoor temperatures and better humidity control.
- Increased Property Value: Homes with high-efficiency HVAC systems often attract more interest in the real estate market. This can increase your home’s resale value, making a high SEER air conditioner a beneficial long-term investment.
- Rebates and Incentives: Many local and federal programs offer rebates or tax credits for installing high-efficiency HVAC systems. These incentives can help offset the initial higher cost of units with high SEER ratings.
Factors Affecting SEER Ratings
Several factors can influence the SEER rating of an air conditioning unit, impacting its efficiency and overall performance:
- Unit Size: The size of the air conditioner should be appropriate for the space it needs to cool. An oversized or undersized unit can reduce efficiency, leading to lower SEER ratings. Proper sizing ensures optimal performance.
- Installation Quality: Improper installation can significantly affect the efficiency of an air conditioner. Factors such as ductwork quality, refrigerant charge, and airflow must be correctly adjusted to achieve the advertised SEER rating.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is crucial for maintaining high efficiency. This includes cleaning or replacing air filters, checking refrigerant levels, and ensuring that all components are functioning correctly. Neglecting maintenance can lead to decreased performance and lower SEER ratings.
- Local Climate: The effectiveness of a SEER rating can also depend on the local climate. In regions with extreme temperatures, the air conditioner may need to work harder than the conditions under which the SEER rating was calculated, potentially lowering its effective efficiency.
- Age of the Unit: Over time, air conditioners may lose efficiency due to wear and tear. Older units typically have lower SEER ratings than newer models due to advancements in technology and design.
Maintaining High SEER Performance
To ensure that your air conditioner continues to operate at its optimal SEER rating, regular maintenance and attentive care are essential. Here are some key practices to maintain high SEER performance:
- Regular Filter Changes: One of the simplest yet most effective ways to maintain efficiency is by regularly changing or cleaning the air filters. Clogged or dirty filters restrict airflow and reduce system efficiency, forcing your unit to work harder.
- Scheduled Professional Maintenance: Have a qualified HVAC technician inspect and service your air conditioner at least once a year. This should include checking the refrigerant levels, cleaning the condenser coils, and ensuring all electrical connections are secure.
- Sealing and Insulating Ductwork: Leaky ducts can significantly reduce the efficiency of your air conditioning system. Ensure that all ductwork is well-sealed and insulated, particularly in unconditioned spaces like attics or basements.
- Thermostat Settings: Use a programmable thermostat to reduce the cooling load on your air conditioner during times when you are not home or when cooling demands are lower. This can help maintain efficiency and reduce wear on the system.
- Upgrading Old Equipment: If your air conditioner is old and less efficient, consider upgrading to a newer model with a higher SEER rating. This can dramatically improve your home’s energy efficiency and reduce operating costs.
FAQs:
In general, yes! A higher SEER rating means a more efficient system, which translates to lower energy bills. However, there can be a higher upfront cost associated with a high-SEER unit. You’ll need to consider your climate, budget, and how long you plan to stay in your home to decide if the potential savings outweigh the initial investment.
Minimum SEER standards are set by the government and vary depending on where you live. But in general, a SEER rating of 14 or higher is considered good. There are even higher-efficiency models available, but they may not be the most cost-effective option for everyone.
The amount you can save depends on several factors, including your current system’s efficiency, your local climate, and your energy usage. Upgrading from a low-SEER unit to a high-SEER one can potentially lead to significant savings on your energy bills.
Many government agencies and utility companies offer rebates or tax credits to encourage homeowners to purchase high-efficiency appliances like air conditioners. Check with your local government or utility provider to see if any programs are available in your area.
Generally, there’s no significant difference in maintenance requirements based on SEER rating. Regular maintenance is crucial for any air conditioner to function efficiently regardless of its SEER score.
SEER rating focuses on efficiency, not cooling power. A high-SEER unit will remove the same amount of heat from your home as a lower-SEER unit with the same BTU rating. The difference is the high-SEER unit will use less energy to achieve that cooling.
While SEER is an important factor, consider other aspects like system size (BTU rating) to ensure it matches your home’s cooling needs. Think about features like variable-speed operation for quieter operation and potentially increased efficiency. Finally, factor in the warranty offered by the manufacturer.
Conclusion
A high SEER rating means better efficiency and cost savings. It’s an important number to consider when buying an air conditioner. Look for higher SEER ratings to get the most out of your investment.

