Ever clicked on a file or folder and watched your cursor spin endlessly, only to be met with a frozen File Explorer? It’s frustrating, especially when you’re trying to get something done. Maybe you’re in a rush to finish a project, or you simply want to access your favorite photos. Whatever the reason, a frozen File Explorer can be a major inconvenience.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the common causes of File Explorer freezing and provide simple, step-by-step solutions to help you get back to work. Whether you’re a tech novice or a seasoned user, these tips will have you up and running in no time. We’ll cover everything from common software conflicts to hardware issues, so you can troubleshoot the problem effectively. Let’s get started…
Outline
Toggle- What Is File Explorer On Windows?
- Why Is File Explorer Not Responding On My Windows PC?
- How To Fix File Explorer Not Responding Error On Windows 11/10?
- Fix – 1: Restart Your File Explorer With Task Manager
- Fix – 2: Restart Your File Explorer With Command Prompt
- Fix – 3: Clear Windows Explorer History
- Fix – 4: Change Your Windows Display Settings
- Fix – 5: Clear System Space
- Fix – 6: Scan For Viruses And Malware
- Fix – 7: Run System File Scanner (SFC)
- Fix – 8: Uninstall Unused Programs
- Fix – 9: Create New User Account
- Fix – 10: Check For Updates
- Fix – 11: Restore Your Windows OS To Previous Version
- FAQs:
- Conclusion
What Is File Explorer On Windows?
File Explorer also known as Windows Explorer is a file management tool embedded within Windows that allows users to navigate, organize, and manage files and folders on their computer. It serves as the primary interface for interacting with all the data stored on a Windows machine, from documents and images to software applications and external storage devices.
The interface of File Explorer is designed to provide an intuitive way to access different parts of the operating system. On the left side of the window, the Navigation Pane offers quick access to commonly used folders like Documents, Downloads, and Pictures, as well as connected devices and network locations. The central pane displays the contents of the selected folder or drive, showing files and subfolders, while the top features a Ribbon or Menu Bar that includes various options for managing files, such as copying, moving, renaming, or deleting them.
File Explorer also integrates several advanced features, such as the Search Box that allows users to quickly locate specific files or folders by name or by using metadata tags. It supports different viewing options, including detailed lists, icons, and thumbnails, enabling users to see their files in the most convenient format.
Beyond file management, File Explorer handles the launching of programs, the management of permissions, and the navigation of network resources. It’s also where you can manage connected devices, such as USB drives, external hard drives, and network-attached storage.
Overall, File Explorer acts as the gateway to everything stored on a Windows system, providing a structured and accessible way to handle data, programs, and devices.
Why Is File Explorer Not Responding On My Windows PC?
File Explorer can become unresponsive on a Windows PC for several reasons, many of which are related to system performance, software conflicts, or issues within the operating system itself. Understanding these causes can help in diagnosing and fixing the problem effectively. Here’s a quick look at the reasons:
- System Overload: One common reason is system overload. When a computer is running too many processes simultaneously, the system’s resources—such as CPU and memory—can become overextended. File Explorer may stop responding if the system is unable to allocate sufficient resources to manage the file management tasks.
- Corrupted System Files: Another cause is corrupted system files. Over time, files that are essential to the operation of Windows may become damaged due to software installations, sudden shutdowns, or malware attacks. These corrupted files can interfere with the normal functioning of File Explorer, causing it to freeze or crash.
- Conflicting Software: Conflicting software is another frequent culprit. Third-party programs, especially those related to file management or system optimization, may conflict with File Explorer. Such software can alter system settings or file associations, leading to instability in File Explorer operations.
- Insufficient Disk Space: Insufficient disk space can also contribute to the problem. If the drive that Windows is installed on is nearly full, File Explorer may struggle to perform basic functions, as there is not enough space to create temporary files or manage data efficiently.
- Outdated Drivers: Outdated or incompatible drivers can also cause File Explorer to become unresponsive. Drivers are software components that allow the operating system to communicate with hardware devices. If these drivers are outdated, missing, or corrupted, File Explorer might encounter difficulties in accessing or displaying files correctly.
- Malware Or Viruses: Malicious software can cause a wide range of issues on a Windows PC, including causing File Explorer to become unresponsive. Malware can alter system files or consume significant resources, leading to performance issues.
- Display Settings Issues: Certain display settings, particularly those involving high DPI (dots per inch) scaling, can cause File Explorer to behave erratically. This is especially common when switching between monitors with different resolutions or scaling settings.
- Excessive Cache Or History: Lastly, Windows Explorer history and cache files can accumulate over time, leading to performance issues. If the history or cache is too large or contains corrupted entries, it can slow down or freeze File Explorer.
Identifying the root cause of File Explorer not responding on your Windows PC is the first step toward fixing the problem. Each of these potential causes can be addressed with specific troubleshooting steps, which I’ll cover in the next sections.
How To Fix File Explorer Not Responding Error On Windows 11/10?
When File Explorer stops responding on a Windows PC, it can disrupt your workflow and cause frustration. Fortunately, there are several methods to resolve this issue. From restarting the application to more advanced troubleshooting steps, these solutions will help you restore File Explorer to full functionality. Below, we’ll guide you through the different approaches to fix the problem, ensuring you can get back to managing your files smoothly.
Fix – 1: Restart Your File Explorer With Task Manager
One of the simplest and most effective ways to fix an unresponsive File Explorer is by restarting it through Task Manager. This method refreshes the application without requiring a full system reboot, allowing you to quickly regain access to your files. To do this:
- Open Task Manager: Press “Ctrl + Shift + Esc” to directly open Task Manager, or use Ctrl + Alt + Delete and select Task Manager from the options menu.
- Locate Windows Explorer: In Task Manager, go to the “Processes” tab. Look for Windows Explorer in the list of active processes.
- End Task: Right-click on Windows Explorer and select “End Task” from the context menu. This action will close File Explorer and stop any processes associated with it.

- Run A New Task: At the top of Task Manager, locate and click on “Run new task”.
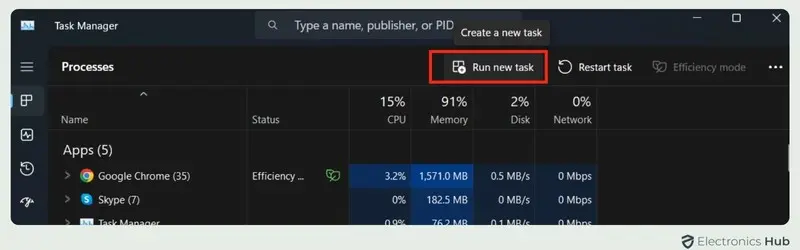
- Restart File Explorer: In the Create New Task window that appears, type “explorer.exe” into the search field and click “OK”. This command will restart File Explorer.

Also Read: How To Kill A Process On Windows?
Fix – 2: Restart Your File Explorer With Command Prompt
If File Explorer is not responding, another effective way to restart it is by using the Command Prompt. This method is slightly more advanced but offers a direct approach to ending and restarting the File Explorer process. Here’s how to do it step by step:
- Open Command Prompt As Administrator: Click on the Start menu and type Cmd in the search bar. When Command Prompt appears in the results, right-click on it and select Run as administrator.
- End The File Explorer Process: In the Command Prompt window, type the following command:
|
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe |

Press Enter after typing the command. This command will forcefully terminate the current File Explorer process, closing any open Windows Explorer windows.
- Restart File Explorer: To restart File Explorer, type the following command:
|
start explorer.exe |

Press Enter again. This command will launch a new instance of File Explorer, refreshing the application and resolving any issues it was experiencing.
Fix – 3: Clear Windows Explorer History
Clearing the Windows Explorer history can help resolve issues when File Explorer is not responding. Over time, the history and cache stored by File Explorer can become cluttered or corrupted, leading to performance issues. Here’s how you can clear the File Explorer history:
- Open Control Panel: Click on the Start menu and type “Control Panel” into the search bar. When the Control Panel appears in the search results, click on it to open the window.
- Access File Explorer Options: Within the Control Panel, locate and click on “File Explorer Options”. This option is sometimes labeled as Folder Options in older versions of Windows.

- Navigate To Privacy Section: In the File Explorer Options window, ensure you are on the “General” tab. Scroll down to the “Privacy” section, which is located towards the bottom of the window.
- Clear File Explorer History: In the Privacy section, you will see an option labeled “Clear File Explorer History” with a “Clear” button next to it. Click on the “Clear” button to remove the history and cache stored by File Explorer.

- Apply And Close: After clearing the history, click on “Apply” and then “OK” to close the File Explorer Options window.
Once you have completed these steps, try opening File Explorer again.
Fix – 4: Change Your Windows Display Settings
You may wonder, what do Display Settings have to do with File Explorer not responding? Surprisingly, incorrect or incompatible display settings can sometimes cause File Explorer to behave erratically, leading to slow performance or crashes. Adjusting your Windows display settings to the recommended configuration can often resolve these issues. Here’s how to do it:
- Open Settings: Press the Windows key + I together to open the Settings menu.
- Navigate To System Tab: In the Settings window, switch to the “System” tab from the left-hand menu. This section controls various system settings, including display options.
- Access Display Settings: Click on “Display” within the System tab to access the Display Settings menu. Here, you can adjust various aspects of your screen’s display, such as resolution, scaling, and orientation.
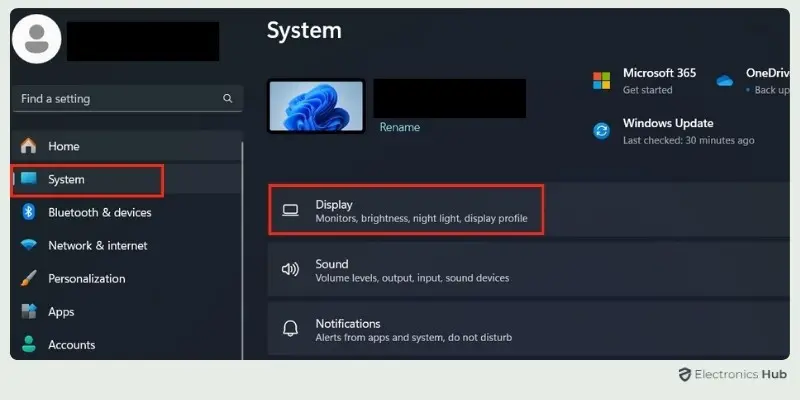
- Adjust To Recommended Settings: In the Display Settings menu, look for the Resolution and Scale and Layout options. Set these to the Recommended values provided by Windows. If your display settings are already set to custom values, consider resetting them to the recommended settings to ensure compatibility with File Explorer.

- Restart File Explorer: Once the changes are applied, it’s a good idea to restart File Explorer to see if the issue has been resolved.
Fix – 5: Clear System Space
Lack of available disk space can lead to various issues, including File Explorer not responding or operating slowly. Clearing up system space by removing unnecessary files can help improve the performance of File Explorer. Here’s how you can do it using the Disk Cleanup tool:
- Open Disk Cleanup: Click on the search bar in the Taskbar at the bottom of the screen and type Disk Cleanup. Select Disk Cleanup from the search results to open the tool.
- Choose A Drive: When the Disk Cleanup tool opens, you will be prompted to select a drive to clean up. Typically, you should choose the “C: drive”, as it usually contains the operating system and most of the system files. Select the drive and click OK.

- Select Files To Delete: The tool will analyze the selected drive and present a list of file categories that can be deleted, such as Temporary Files, System Cache, Recycle Bin contents, and more. Review the list and check the boxes next to the types of files you want to delete.

- Start Cleanup: Once you’ve selected the files to delete, click on “OK” to start the cleanup process. You may be asked to confirm your decision. Click Delete Files to proceed.
- Wait For The Cleanup To Complete: The Disk Cleanup tool will begin deleting the selected files. Depending on the amount of data and the speed of your system, this process may take a few minutes.
By clearing up system space, you reduce the load on your Windows PC, which can help resolve issues where File Explorer is not responding or is slow to operate.
Fix – 6: Scan For Viruses And Malware
Viruses and malware can significantly impact your system’s performance, often causing issues like File Explorer not responding, Windows Explorer crashing, or other unexpected behavior. Running a thorough scan for malicious software is an important step in resolving these problems. Here’s how you can do it:
- Open Windows Security: Click on the Start menu and type Windows Security into the search bar. Select Windows Security from the search results to open the tool.
- Access Virus & Threat Protection: In the Windows Security window, navigate to the “Virus & Threat Protection” tab.

- Run A Quick Scan: To start with, click on “Quick Scan”. This will scan the most vulnerable areas of your system where malware is often found. The scan will only take a few minutes and will identify any immediate threats.

- Perform A Full Scan: For a more comprehensive check, click on Scan options below the Quick Scan button, then select Full Scan. This scan will take longer as it checks all files and running programs on your hard drive, ensuring no threats are missed.
- Review And Remove Threats: Once the scan is complete, Windows Security will display the results. If any threats are found, you will be given options to Quarantine or Remove them. Follow the prompts to eliminate any detected malware or viruses from your system.
- Restart Your PC: After removing any threats, it’s a good idea to restart your PC.
Keeping your system clean and secure is essential for maintaining smooth and reliable performance.
Fix – 7: Run System File Scanner (SFC)
Corrupted or missing system files can cause File Explorer to malfunction, resulting in it not responding or Windows Explorer crashing. The System File Checker (SFC) is a built-in tool in Windows that scans for and repairs these corrupted system files. Running an SFC scan can often resolve issues with File Explorer. Follow these steps to run the SFC scan:
- Open Command Prompt As Administrator: Click on the Start menu and type Cmd in the search bar. When Command Prompt appears in the search results, right-click on it and select Run as administrator.
- Run The SFC Scan: In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
|
sfc /scannow |

The SFC tool will start scanning your system for corrupted or missing files. This process may take some time, so be patient and allow the scan to complete without interruption.
- Wait For The Scan To Complete: The SFC tool will automatically repair any corrupted or missing files it finds. You’ll see a message in the Command Prompt window indicating the scan results once it’s finished. If any issues are found and fixed, the tool will notify you.
- Restart Your PC: After the SFC scan is completed and any necessary repairs are made, restart your computer.
Running the System File Checker (SFC) helps address problems where File Explorer is not responding due to corrupted or damaged system files.
Fix – 8: Uninstall Unused Programs
Unused or outdated programs can take up valuable system resources and potentially cause issues like File Explorer not responding. Removing these unnecessary programs can help free up space and improve your system’s performance. Here’s how to uninstall unused programs:
- Open Control Panel: Click on the Start menu, type Control Panel in the search bar, and select it from the search results.
- Access Programs And Features: In the Control Panel window, locate and click on “Programs and Features”. This section lists all the software installed on your Windows system.
- Find The Program To Uninstall: Scroll through the list of installed programs and identify the ones you no longer need or use.

- Uninstall The Program: Right-click on the program you wish to remove and select “Uninstall” from the context menu. Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the uninstallation process.

- Repeat If Necessary: If you have multiple programs to uninstall, repeat the above steps for each one.
- Restart Your PC: After uninstalling unused programs, it’s a good idea to restart your PC. This ensures that all changes are fully applied and can help improve the responsiveness of File Explorer.
Fix – 9: Create New User Account
If File Explorer continues to malfunction despite other fixes, creating a new user account can be a helpful solution. Sometimes, user-specific settings or corrupt profiles can cause issues, and starting fresh with a new account can resolve them. Here’s how to create a new user account on Windows:
- Open Settings: Press the Windows key + I to open the Settings menu.
- Navigate To Accounts: In the Settings window, select Accounts from the list of options. This section manages all user accounts on your Windows system.
- Access “Other Users”: On the left-hand menu, click on “Other users”. This section allows you to add new accounts to your system.

- Add A New Account: Under Other users, click on “Add account”.
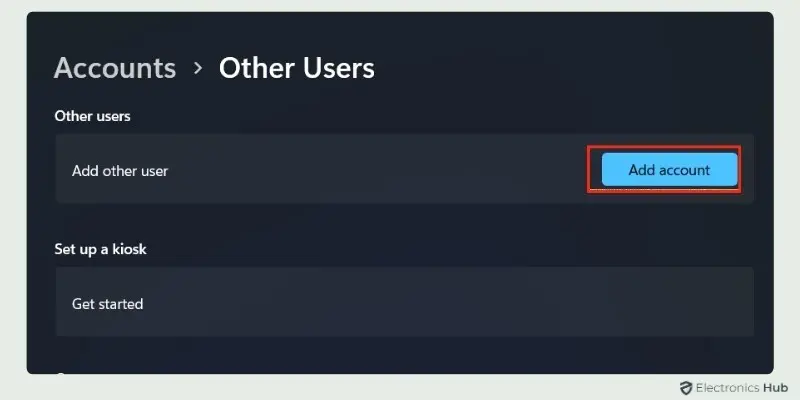
- Then “Choose I don’t have this person’s sign-in information”, if you want to create a local account. Then select Add a user without a Microsoft account.

- Create Account Details: Enter the username and password for the new account, and fill in the required security questions. Click Next to complete the process.
- Switch To The New Account: Once the new account is created, sign out of your current account and sign in with the new one.
- Test File Explorer: After logging into the new account, open File Explorer to check if the issues have been resolved.
Fix – 10: Check For Updates
Ensuring that your Windows system is up to date can help resolve issues like File Explorer not responding or Windows Explorer crashing. Updates often include patches, bug fixes, and improvements that can enhance the stability of your system. Here’s how to check for updates:
- Navigate To Windows Update: In the Settings window, click on “Windows Update”. This section manages all updates for your Windows operating system.
- Check For Updates: Under the Windows Update tab, click on “Check for updates”. Windows will start searching for any available updates, including those for File Explorer and other system components.

- Download And Install Updates: If updates are found, they will be listed. Click on Download to start the process, and then Install once the download is complete. Some updates may require a system restart to fully apply the changes.
- Restart Your PC: After the updates are installed, restart your PC if prompted. This ensures that all changes are fully integrated into the system.
- Test File Explorer: Once your system has rebooted, open File Explorer to check if the issue has been resolved.
Also Read: Desktop Icons Are Missing On Windows
Fix – 11: Restore Your Windows OS To Previous Version
If File Explorer is still not responding or if other issues persist, restoring your Windows OS to a previous version can be an effective solution. System Restore allows you to revert your computer’s state to a point in time when everything is functioning correctly. Here’s how to perform a System Restore:
- Open System Restore: Click on the Start menu, type Create a restore point into the search bar, and select it from the search results. This will open the System Properties window.
- Access System Restore: In the System Properties window, click on the “System Restore” button. This will launch the System Restore wizard.

- Choose A Restore Point: In the System Restore wizard, click “Next” to view a list of available restore points. Select a restore point that predates the issues with File Explorer or any other problems you are experiencing. You can also click Scan for affected programs to see which applications and drivers will be affected by the restore.

- Confirm Restore Point: After selecting a restore point, click Next and then Finish to confirm your choice. Windows will then begin the restoration process, which may take some time.
- Restart Your PC: Once the System Restore is complete, your PC will restart automatically.
- Check File Explorer: After your PC has rebooted, open File Explorer to verify if the issue has been resolved.
Using System Restore can effectively resolve issues where File Explorer is not working by reverting your system to a stable state before the problems begin.
FAQs:
To disable Quick Access:
* Open File Explorer Options.
* Under the “General” tab, change “Open File Explorer to:” from “Quick Access” to “This PC.”
* Uncheck the boxes under the Privacy section for showing recent files and frequently used folders.
Restarting File Explorer involves stopping and restarting the File Explorer process, which can fix minor, temporary issues.
Resetting File Explorer typically involves resetting File Explorer’s settings to their defaults, which can help if the problem is caused by misconfigured settings.
To prevent future issues:
* Keep your Windows system and drivers up to date.
* Avoid overloading File Explorer with too many open windows or tabs.
* Regularly clear File Explorer history.
* Be cautious about installing third-party software that might interfere with system processes.
File Explorer may freeze when accessing network drives due to slow network connections, incorrect drive mappings, or issues with the remote server. Ensuring a stable network connection and verifying the status of the network drive can help resolve these freezes.
If File Explorer opens automatically on startup and you want to prevent this:
* Check your Startup folder by typing shell:startup in the Run dialog (Windows + R).
* Remove any shortcuts to File Explorer.
* Disable any related startup tasks in Task Manager.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the “File Explorer Not Responding” error on Windows can be caused by various factors, including corrupted system files, overloaded system resources, faulty hardware, and third-party software conflicts. By following the troubleshooting steps outlined in this blog post, you should be able to resolve the issue and restore the functionality of your File Explorer.

