Ever had that frustrating moment when your PC just won’t boot up? Or maybe it’s running slower than a snail. Sometimes, the solution to these problems lies in a tiny piece of software called BIOS. It’s like the brain of your computer, controlling everything from hardware to boot-up sequence.
But what happens when your BIOS is outdated? Well, it’s like trying to drive a car with a flat tire – it’s just not going to work well. That’s why updating your BIOS is so important.
In this simple guide, we’ll walk you through the steps of updating your BIOS, step by step. We’ll cover everything from finding the right update to safely flashing it onto your motherboard. By the end, you’ll be able to update your BIOS with confidence and hopefully solve those pesky computer problems.
Outline
ToggleWhat Is BIOS?
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is firmware embedded in a chip on the motherboard of your computer. It controls the boot process, performing hardware checks and initializing components like the CPU, RAM, and storage devices before the operating system starts. Without a properly functioning BIOS, the computer can’t communicate with its hardware, meaning it won’t boot or recognize key devices. BIOS also determines the boot order, which defines whether the system should boot from the hard drive, USB drive, or CD/DVD first.
When you turn on your computer, BIOS runs a Power-On Self-Test (POST) to ensure all hardware components are working correctly. It then loads the bootloader, which initiates the operating system. The configuration for BIOS settings can usually be accessed by pressing a specific key (like F2 or DEL) during startup. These settings let users manage important configurations like system time, boot order, and hardware monitoring.
More recent computers have shifted toward UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), a modern replacement for BIOS that offers enhanced functionality. While BIOS is limited in terms of storage and hardware support, UEFI allows for larger storage drives, faster boot times, and a graphical interface for easier navigation. UEFI also supports secure boot, which helps prevent malware from infecting the boot process.
The transition from BIOS to UEFI gives systems more flexibility and improved performance, particularly in modern computing environments.
Why Do You Need To Update Your PC’s BIOS?
Updating your PC’s BIOS can seem unnecessary, especially if your system is running smoothly. However, there are several reasons why performing a BIOS update may be important. Manufacturers regularly release new BIOS updates to address bugs, improve hardware compatibility, and enhance performance. These updates often come with critical fixes that help the system run more efficiently, resolve stability issues, or enable support for new processors, memory, and other components.
- Improved Hardware Compatibility: Updating the BIOS can add support for new hardware, such as CPUs, RAM, and storage devices. This ensures that the new components work without issues.
- Bug Fixes And Stability Improvements: Manufacturers release BIOS updates to address bugs or system glitches that can cause crashes, freezes, or performance problems.
- Security Enhancements: Older BIOS versions may have security vulnerabilities. An update can patch these issues, helping protect your system from malicious software or attacks that target the boot process.
- New Features: Some BIOS updates bring new features like advanced power-saving modes, fan control improvements, or support for new technologies such as UEFI features or secure boot options.
- Enhanced Performance: In some cases, BIOS updates can improve the overall performance of your system by optimizing hardware communication or enhancing system efficiency.
- Fixing Boot Issues: If your system is experiencing trouble booting up or recognizing hardware, updating the BIOS may resolve those issues.
How To Update Your PCs BIOS?
To safely update your PC’s BIOS, it is crucial to follow a precise process and use the correct update tailored to your motherboard model. Using an inappropriate update could cause your system to malfunction. Here’s how you can ensure you’re applying the right update to your system:
Before starting the process, make sure to back up important data, as the update process can sometimes reset settings or, in rare cases, lead to system failures. You’ll also need access to a stable power source and a USB drive in many cases, depending on the method used.
Step – 1: Gather Necessary Information
First, ensure you collect key details about your system, such as the current BIOS version and the motherboard model. This information is crucial to ensure you download the correct BIOS update for your system.
Here’s how you can gather the relevant details:
Method 1: Using System Information In Windows
- Press the “Windows key + R” to open the Run dialog box.
- In the box, type “msinfo32” and press Enter. This will open the System Information window.

- In the System Summary section, find the entry labeled “BIOS Version/Date.” Here, you’ll see your current BIOS version, the release date, and the name of the manufacturer.

- Take note of this information as you’ll need it when downloading the correct BIOS update.
Method 2: Through BIOS Or UEFI Menu
You can also find the BIOS version by entering the BIOS or UEFI menu directly. Here’s how:
- Restart your PC.
- As it boots up, press the designated key (usually F2, DEL, F12, or F10) to enter the BIOS or UEFI settings menu.
- Once inside, look for the BIOS Information or System Information section, which will display your BIOS version and manufacturer details.
Using the wrong BIOS update can lead to system failures or render your motherboard unusable. Installing an incompatible version might cause your computer to fail to boot, as the system will not recognize the new firmware. Gathering the correct information ensures you’re using the right update, protecting your PC from issues during the process.
Step – 2: Find And Download BIOS Update
Once you have gathered the necessary information about your current BIOS version and motherboard manufacturer, the next step is to find and download the correct BIOS update. Each motherboard manufacturer provides updates through their official website, so it’s important to download the firmware specifically made for your motherboard model.
- Visit The Manufacturer’s Website: Go to the official website of your motherboard’s manufacturer. Common manufacturers include Dell, ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, and HP.
- Navigate To The Support Or Downloads Section: Look for the support or downloads section, which is usually located in the main menu or under the “Support” tab.
- Enter Your Motherboard Model: Use the model number of your motherboard (which you gathered earlier) to search for the correct BIOS update. Some websites may require you to enter a Service Tag or other identification numbers.
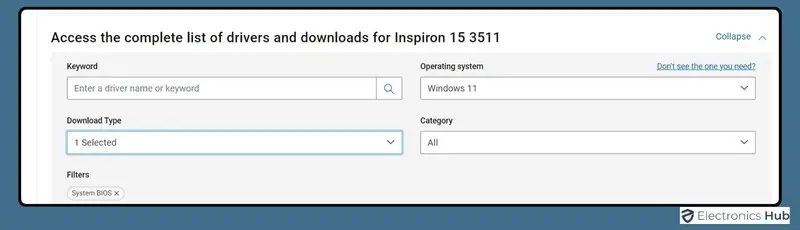
- Download The Latest BIOS Version: Once you find the update for your specific model, download the latest BIOS version to your computer. Make sure that the version you’re downloading is newer than your current version and compatible with your system.
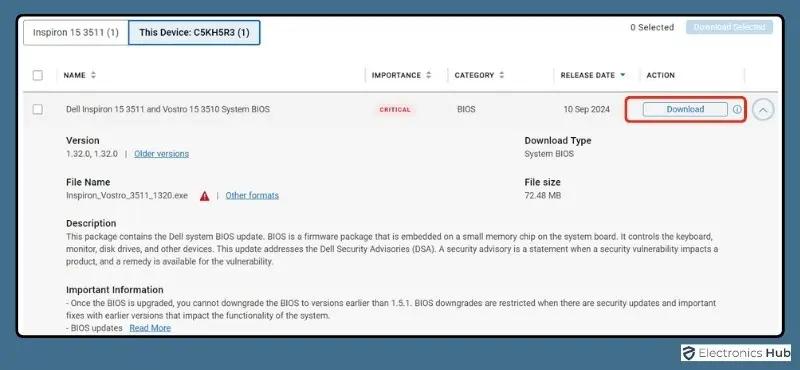
- Review The Release Notes: Before proceeding, read the release notes to see what changes or improvements have been made in the new BIOS update. These notes often provide important information regarding compatibility or additional steps.
However, If your manufacturer lists two or more BIOS updates, it’s important to install them gradually. For example, if the site shows BIOS version 1.1 and BIOS version 1.2, and you are on version 1.0, install version 1.1 first, then update to version 1.2.
Skipping versions may lead to compatibility issues, especially if the skipped update contains important fixes or changes that newer updates depend on. This ensures a smoother transition between updates and reduces the risk of bricking your motherboard.
Note: The process of downloading a BIOS update varies depending on the motherboard manufacturer. Ensure that you follow the instructions provided on their website to avoid any issues during the download process.
Step – 3: Transfer BIOS Update File To USB Drive
After downloading the BIOS update file, it’s time to prepare a USB drive to transfer the file and use it for the update process. Most BIOS update files are compressed in a ZIP format, so you’ll need to extract them before proceeding.
Steps To Prepare And Transfer The BIOS Update File:
- Extract The ZIP File: Once the BIOS update file is downloaded, locate the file and right-click on it to choose Extract All. This will create a folder with the extracted contents.
- Examine The Extracted Files: In the extracted folder, you’ll typically find the BIOS update file (with a .CAP or .ROM extension) and sometimes a readme.txt file. The readme file often contains important instructions from the manufacturer. Take a moment to review it.
- Use A FAT32 Formatted USB Drive: The USB drive used for the update must be formatted in FAT32. If your USB drive is not formatted this way:
- Open File Explorer and right-click the USB drive.
- Select Format from the menu.
- In the File System dropdown, choose FAT32 and click Start.
- Be aware that formatting will erase all data on the USB drive.
- Copy The BIOS Update File: After formatting, copy the extracted BIOS update file (e.g., .CAP or .ROM) directly to the root directory of the USB drive. Make sure not to place the file inside any folders, as doing so may prevent the system from detecting it during the update.
By placing the BIOS update file on the root of a properly formatted USB drive, you’ll ensure that your system can recognize the file during the update process, allowing for a smooth and error-free update.
Step – 4: Update Your BIOS
Now that the BIOS update file is ready on the USB drive, it’s time to perform the actual BIOS update. This step requires caution, as any interruptions (such as power loss) during the update can cause system issues. Make sure your computer is connected to a stable power source.
Here’s how to proceed with updating your BIOS using the USB drive:
- Restart Your Computer: Begin by restarting your PC. As soon as the system starts to boot, press the key that opens the BIOS setup utility (usually F2, DEL, or F10 depending on your motherboard).
- Enter The BIOS Or UEFI Settings: Once in the BIOS menu, navigate using your keyboard to locate the section for BIOS updates. It may be labeled as EZ Flash, Q-Flash, or similar, depending on your motherboard manufacturer.
- Select The BIOS Update Option: Within the BIOS update utility, choose the option to update using a USB drive. The system will prompt you to locate the BIOS update file on the USB drive.
- Choose The BIOS Update File: Select the BIOS update file (usually a .CAP or .ROM file) from the root directory of your USB drive.
- Start The Update: Once the correct file is selected, confirm the update. The system will begin the update process, during which it will erase the old BIOS and install the new one.

- Wait For The Update To Complete: During the update, the system may restart several times. Do not turn off your computer or remove the USB drive until the process is complete. Interruptions can corrupt the update and damage the system.
- Restart The Computer: After the update is finished, the system will automatically restart. Upon rebooting, your PC should boot up using the updated BIOS version. You can confirm the update by entering the BIOS menu again and checking the version.
Also Read: What is CSM BIOS?
Other Ways To Update BIOS
In addition to using a USB drive, there are other methods to update your BIOS, each offering a different level of convenience depending on your system and motherboard. Some modern motherboards come with features that allow you to update the BIOS even without an operating system, while others provide software tools for updates directly within Windows.
Update Your BIOS Through BIOS Flashback
BIOS Flashback is a feature available on many modern motherboards that allows you to update the BIOS without the need for a working CPU, memory, or operating system. This method is useful when building a new system or troubleshooting an older one that can’t boot. It provides a way to recover or update the BIOS using only a USB drive and the BIOS Flashback button on the motherboard.
- Prepare The USB Drive: As with the traditional method, format the USB drive in FAT32 and copy the BIOS update file (usually a .CAP or .ROM file) to the root directory. Make sure the file is named according to the manufacturer’s instructions for BIOS Flashback. The correct file name is usually specified in the user manual.
- Power Off The System: Turn off the PC completely and disconnect it from the power supply. If the system is already built, make sure all components are securely connected.
- Insert The USB Drive: Plug the USB drive with the BIOS update file into the designated BIOS Flashback USB port on the motherboard. This port is often labeled on the back panel.
- Press The BIOS Flashback Button: Locate the BIOS Flashback button on the motherboard. Press and hold the button for a few seconds until the BIOS Flashback LED starts blinking. This indicates that the BIOS update process has started.
- Wait For The Process To Complete: The LED will continue to blink while the BIOS update is being installed. Do not turn off the system or remove the USB drive during this time. Once the process is complete, the LED will stop blinking.
- Power On The System: After the update is done, reconnect the power supply and turn on the system. The updated BIOS will now be installed, and the system should boot up successfully.
BIOS Flashback is a convenient recovery method that bypasses the need for a functioning operating system, allowing you to update the BIOS in situations where traditional methods might fail.
To know more about updating BIOS without CPU, read the article How to Update BIOS Without CPU.
Update Your BIOS Through Windows Software
Another convenient way to update your BIOS is through the manufacturer’s software directly within Windows. Many motherboard manufacturers provide dedicated utilities that allow you to update the BIOS without leaving the operating system. This method is often quicker and easier, especially for users who are uncomfortable navigating the BIOS interface.
- Download The Manufacturer’s Update Tool: Visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website and download their BIOS update utility for Windows. Common tools include ASUS EZ Update, MSI Live Update, and Gigabyte @BIOS.
- Install The Tool: Once downloaded, install the utility on your system by following the on-screen instructions.
- Run The Update Tool: Open the BIOS update utility. Most tools will automatically detect your BIOS version and the latest available update. If not, you may need to manually enter your motherboard model.
- Download The Latest BIOS Version: The tool will provide a prompt to download the latest BIOS update. Confirm the download and the tool will handle the process.
- Start The Update: Once the update is downloaded, the tool will prompt you to begin the update. It may require a system restart.
- Restart Your Computer: After the update completes, the tool will automatically restart your computer. Allow the system to reboot and apply the changes.
Make sure the update process isn’t interrupted, and follow all prompts carefully.
Also Read: How To Force Group Policy Update Remotely?
Troubleshooting Tips If BIOS Can’t Update
In some cases, the BIOS update process may encounter issues, preventing the update from completing successfully. Whether it’s due to an incorrect file, hardware problems, or a corrupted update, there are ways to troubleshoot and resolve the situation.
Here are common troubleshooting tips if your BIOS can’t update:
- Check The BIOS File: Ensure you’ve downloaded the correct BIOS update for your specific motherboard model. An incorrect version can cause the update to fail or the system to become unresponsive. Verify the file extension (e.g., .CAP, .ROM) and confirm that it matches the expected format for your motherboard.
- Reformat The USB Drive: Make sure the USB drive used for the update is formatted to FAT32. Other file systems like NTFS can cause issues during the update process. Try using a different USB drive if the system is not detecting the one you’re using.
- Re-Download The BIOS Update File: If the BIOS file is corrupted or incomplete, the update might fail. Download the file again from the official website and repeat the update process.
- Clear The CMOS: Resetting the CMOS can help resolve issues if your system is stuck or won’t boot after a failed BIOS update. You can usually do this by removing the CMOS battery on the motherboard for a few minutes, then reinstalling it. Some motherboards also have a CMOS reset jumper or button, which can be used to restore factory settings.
- Ensure Stable Power Supply: A power outage or system crash during the BIOS update can cause the update to fail. Always ensure your computer is connected to a stable power source or use a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) to avoid interruptions.
- Use BIOS Flashback: If the system won’t boot or the BIOS update continues to fail, try using BIOS Flashback if your motherboard supports it. This method allows you to update the BIOS without needing a functional system.
- Update Gradually: If multiple BIOS updates are available, ensure you update each version step by step instead of skipping versions. Skipping intermediate versions can lead to compatibility issues.
Also Check:
FAQs:
Yes, updating the BIOS can be risky if not done correctly. A failed update can result in a non-functional computer (bricking). Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions closely and ensure your PC stays powered during the process.
Check your motherboard manufacturer’s website for any BIOS update releases. They usually provide details on what the update addresses. Only proceed if the update solves an issue you are facing or improves compatibility with new hardware.
No, you don’t need to reinstall your operating system after a BIOS update. However, it’s essential to reset your BIOS settings correctly afterward to avoid potential system configuration issues.
Yes, BIOS updates often address hardware compatibility issues, especially when using newer CPUs, memory, or peripherals that weren’t supported at the time of the initial BIOS release.
If your BIOS update fails, refer to your motherboard’s recovery options, such as BIOS Flashback or dual BIOS, if supported. Contact your manufacturer’s support if you cannot recover the BIOS.
Although rare, a failed BIOS update can cause irreparable damage to your motherboard, especially if the update process is interrupted. Always ensure the update is carried out correctly to minimize risks.
Conclusion
Updating your PC BIOS can enhance system performance, improve compatibility with new hardware, and even fix bugs. While it might seem daunting, the process is relatively simple and can be completed with a few clicks. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and back up your BIOS settings before proceeding to avoid any potential issues. By taking these steps, you can ensure that your PC is running at its optimal level. Let us know in the comments if this guide is helpful.

